- 📝 Posted:
- 🚚 Summary of:
- P0258, P0259, P0260, P0261
- ⌨ Commits:
5876755...e8a0b3e,e8a0b3e...dfaa3c6,dfaa3c6...ed9ee93,ed9ee93...ae2fc28- 💰 Funded by:
- Blue Bolt, [Anonymous], Yanga, Splashman
- 🏷 Tags:
And we're back to PC-98 Touhou for a brief interruption of the ongoing Shuusou Gyoku Linux port. Let's clear some of the Touhou-related progress from the backlog, and use the unconstrained nature of these contributions to prepare the 📝 upcoming non-ASCII translations commissioned by Touhou Patch Center. The current budget won't cover all of my ambitions, but it would at least be nice if all text in these games was feasibly translatable by the time I officially start working on that project.
At a little over 3 pushes, it might be surprising to see that this took longer than the 📝 TH03/TH04/TH05 cutscene system. It's obvious that TH02 started out with a different system for in-game dialog, but while TH04 and TH05 look identical on the surface, they only actually share 30% of their dialog code. So this felt more like decompiling 2.4 distinct systems, as opposed to one identical base with tons of game-specific differences on top.
The table of contents was pretty popular last time around, so let's have another one:
- Overview of TH04's dialog system
- Changes introduced in TH05
- Command reference for the TH04 and TH05 systems
- Overview of TH02's dialog system
- TH02's face portrait images
- Bugs during TH02's dialog box slide-in animation
- Bugs and quirks in Mima's defeat dialog (might be lore-relevant)
- TH03 win messages
Let's start with the ones from TH04 and TH05, since they are not that broken. For TH04, ZUN started out by copy-pasting the cutscene system, causing the result to inherit many of the caveats I already described in the cutscene blog post:
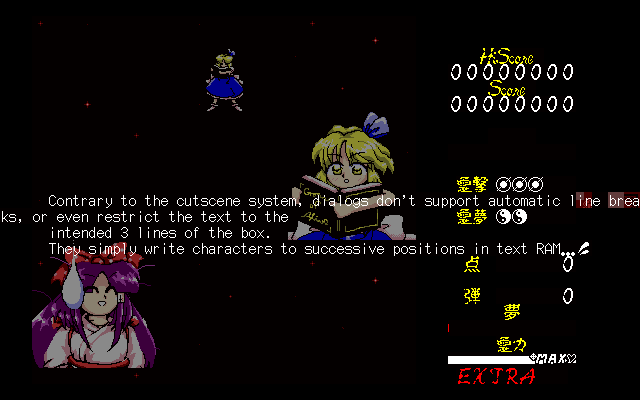
- It's still a plaintext format geared exclusively toward full-width Japanese text.
- The parser still ignores all whitespace, forcing ASCII text into hacks with unassigned Shift-JIS lead bytes outside the second byte of a 2-byte chunk.
- Commands are still preceded by a
0x5Cbyte, which renders as either a\or a¥depending on your font and interpretation of Shift-JIS. - Command parameters are parsed in exactly the same way, with all the same limits.
- A lot of the same script commands are identical, including 7 of them that were not used in TH04's original dialog scripts.
Then, however, he greatly simplified the system. Mainly, this was done by moving text rendering from the PC-98 graphics chip to the text chip, which avoids the need for any text-related unblitting code, but ZUN also added a bunch of smaller changes:
- The player must advance through every dialog box by releasing any held keys and then pressing any key mapped to a game action. There are no timeouts.
- The delay for every 2 bytes of text was doubled to 2 frames, and can't be overridden.
- Instead of holding
ESCto fast-forward, pressing any key will immediately print the entire rest of a text box. - Dialogs run in their own single-buffered frame loop, interrupting the rest of the game. The other VRAM page keeps the background pixels required for unblitting the face images.
- All script commands that affect the graphics layer are preceded by a 1-frame delay. ZUN most likely did this because of the single-buffered nature, as it prevents tearing on the first frame by waiting for the CRT beam to return to the top-left corner before changing any pixels.
- Both boxes are intended to contain up to 30 half-width characters on each of their up to 3 lines, but nothing in the code enforces these limits. There is no support for automatic line breaks or starting new boxes.
0x20
spaces, the text as a whole is still blindly processed two bytes at a
time, and any commands can only appear at even byte positions within a
line. I dimmed the VRAM pixels to 25% of their original brightness to make the
text easier to read.
0x20 spaces
only work at odd byte positions because the game treats them as the
trailing byte of a full-width Shift-JIS codepoint. I don't know how
large the budget for the upcoming non-ASCII translations will be, but
I'm going to fix this even in the very basic fully static variant.
I dimmed the VRAM pixels to 25% of their original brightness to make the
text easier to read.
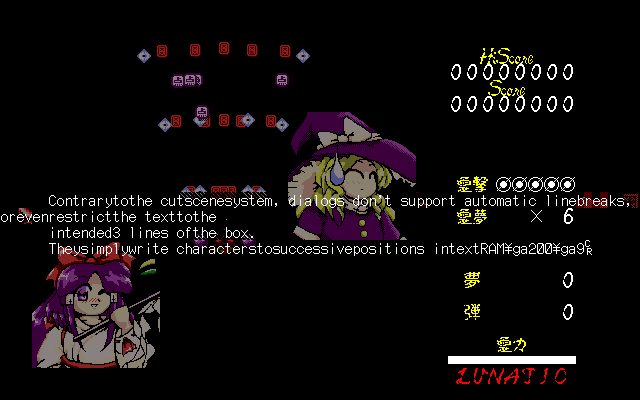
TH05 then moved from TH04's plaintext scripts to the binary
.TX2 format while removing all the unused commands copy-pasted
from the cutscene system. Except for a
single additional command intended to clear a text box, TH05's dialog
system only supports a strict subset of the features of TH04's system.
This change also introduced the following differences compared to TH04:
- The game now stores the dialog of all 4 playable characters in the same
file, with a
(4 + 1)-word header that indicates the byte offset and length of each character's script. This way, it can load only the one script for the currently played character. - Since there is no need for whitespace in a binary format, you can now
use ASCII
0x20spaces even as the first byte of a 2-byte text chunk! 🥳 - All command parameters are now mandatory.
- Filenames are now passed directly by pointer to the respective game
function. Therefore, they now need to be null-terminated, but can in turn be
as long as
📝 the number of remaining bytes in the allocated dialog segment.
In practice though, the game still runs on DOS and shares its restriction of
8.3 filenames…

- When starting a new dialog box, any existing text in the other box is now colored blue.
- Thanks to ZUN messing up the return values of the command-interpreting
switchfunction, you can effectively use only line break and gaiji commands in the middle of text. All other commands do execute, but the interpreter then also treats their command byte as a Shift-JIS lead byte and places it in text RAM together with whatever other byte follows in the script.
This is why TH04 can and does put its\=commandsinto
the boxes started with the0or1commands, but TH05 has to put its0x02commands before the equivalent0x0D.
0x02 byte to text RAM results in an Also note how each face change is now preceded by two frames of delay.
For modding these files, you probably want to use TXDEF from
-Tom-'s MysticTK. It decodes these
files into a text representation, and its encoder then takes care of the
character-specific byte offsets in the 10-byte header. This text
representation simplifies the format a lot by avoiding all corner cases and
landmines you'd experience during hex-editing – most notably by interpreting
the box-starting 0x0D as a
command to show text that takes a string parameter, avoiding the broken
calls to script commands in the middle of text. However, you'd still have to
manually ensure an even number of bytes on every line of text.
In the entry function of TH05's dialog loop, we also encounter the hack that
is responsible for properly handling
📝 ZUN's hidden Extra Stage replay. Since the
dialog loop doesn't access the replay inputs but still requires key presses
to advance through the boxes, ZUN chose to just skip the dialog altogether in the
specific case of the Extra Stage replay being active, and replicated all
sprite management commands from the dialog script by just hardcoding
them.
And you know what? Not only do I not mind this hack, but I would have
preferred it over the actual dialog system! The aforementioned sprite
management commands
effectively boil down to manual memory management,
deallocating all stage enemy and midboss sprites and thus ensuring that the
boss sprites end up at specific master.lib sprite IDs (patnums
). The
hardcoded boss rendering function then expects these sprites to be available
at these exact IDs… which means that the otherwise hardcoded bosses can't
render properly without the dialog script running before them.
![]()
There is absolutely no excuse for the game to burden dialog scripts with
this functionality. Sure, delayed deallocation would allow them to blit
stage-specific sprites, but the original games don't do that; probably
because none of the two games feature an unblitting command. And even if
they did, it would have still been cleaner to expose the boss-specific
sprite setup as a single script command that can then also be called from
game code if the script didn't do so. Commands like these just are a recipe
for crashes, especially with parsers that expect fullwidth Shift-JIS
text and where misaligned ASCII text can easily cause these commands to be
skipped.
But then again, it does make for funny screenshot material if you accidentally the deallocation and then see bosses being turned into stage enemies:
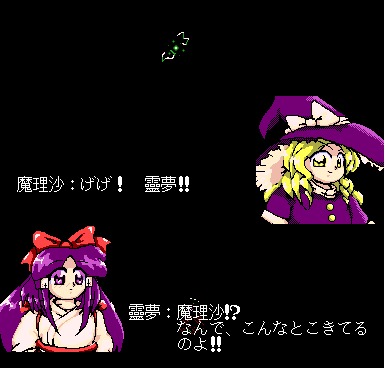
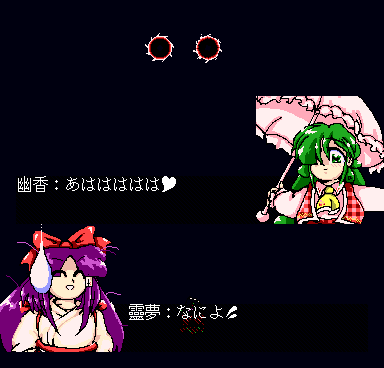
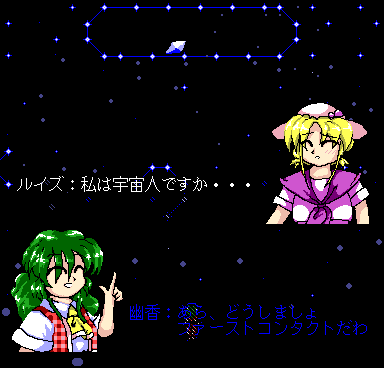
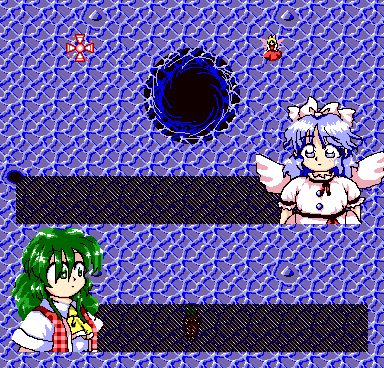

\c /

0x04 command inside a dialog
script.In the case of 4️⃣, the game then even crashes on this frame at the end of the dialog, in a way that resembles the infamous 📝 TH04 crash before Stage 5 Yuuka if no EMS driver is loaded. Both the stage- and boss-specific BFNT sprites are loaded into memory at this point, leaving no room for the 256×256-pixel background image on the size-limited master.lib heap.
With all the general details out of the way, here's the command reference:
| 0 1 |
0x00 0x01 |
Selects either the player character (0) or the boss (1) as the
currently speaking character, and moves the cursor to the beginning of
the text box. In TH04, this command also directly starts the new dialog
box, which is probably why it's not prefixed with a \ as it
only makes sense outside of text. TH05 requires a separate 0x0D command to do the
same. |
| \=1 | 0x02 0x!! | Replaces the face portrait of the currently active speaking character with image #1 within her .CD2 file. |
| \=255 | 0x02 0xFF | Removes the face portrait from the currently active text box. |
| \l,filename | 0x03 filename 0x00 | Calls master.lib's super_entry_bfnt() function, which
loads sprites from a BFNT file to consecutive IDs starting at the
current patnum write cursor. |
| \c | 0x04 | Deallocates all stage-specific BFNT sprites (i.e., stage enemies and
midbosses), freeing up conventional RAM for the boss sprites and
ensuring that master.lib's patnum write cursor ends up at
In TH05's Extra Stage, this command also replaces 📝 the sprites loaded from MIKO16.BFT with the ones from ST06_16.BFT. |
| \d | Deallocates all face portrait images. The game automatically does this at the end of each dialog sequence. However, ZUN wanted to load Stage 6 Yuuka's 76 KiB of additional animations inside the script via \l, and would have once again
run up against the master.lib heap size limit without that extra free
memory. |
|
| \m,filename | 0x05 filename 0x00 | Stops the currently playing BGM, loads a new one from the given file, and starts playback. |
| \m$ | 0x05 $ 0x00 | Stops the currently playing BGM. Note that TH05 interprets $ as a null-terminated filename as well. |
| \m* | Restarts playback of the currently loaded BGM from the beginning. | |
| \b0,0,0 | 0x06 0x!!!! 0x!!!! 0x!! | Blits the master.lib patnum with the ID indicated by the third parameter to the current VRAM page at the top-left screen position indicated by the first two parameters. |
| \e0 | Plays the sound effect with the given ID. | |
| \t100 | Sets palette brightness via master.lib's
palette_settone() to any value from 0 (fully black) to 200
(fully white). 100 corresponds to the palette's original colors. |
|
|
\fo1 \fi1 |
Calls master.lib's palette_black_out() or
palette_black_in() to play a hardware palette fade
animation from or to black, spending roughly 1 frame on each of the 16 fade steps. |
|
|
\wo1 \wi1 |
0x09 0x!! 0x0A 0x!! |
Calls master.lib's palette_white_out() or
palette_white_in() to play a hardware palette fade
animation from or to white, spending roughly 1 frame on each of the 16 fade steps.The TH05 version of 0x09 also clears the text in both boxes
before the animation. |
| \n | 0x0B | Starts a new line by resetting the X coordinate of the TRAM cursor
to the left edge of the text area and incrementing the Y coordinate.
The new line will always be the next one below the last one that was properly started, regardless of whether the text previously wrapped to the next TRAM row at the edge of the screen. |
| \g8 | Plays a blocking 8-frame screen shake animation. Copy-pasted from the cutscene parser, but actually used right at the end of the dialog shown before TH04's Bad Ending. | |
| \ga0 | 0x0C 0x!! | Shows the gaiji with the given ID from 0 to 255 at the current cursor position, ignoring the per-glyph delay. |
| \k0 | Waits 0 frames (0 = forever) for any key to be pressed before continuing script execution. | |
| 0x0D | Starts a new dialog box with the previously selected speaker. All text
until the next 0xFF
command will appear on screen.Inside dialogs, this is a no-op. |
|
| 0x0E | Takes the current dialog cursor as the top-left corner of a
240×48-pixel rectangle, and replaces all text RAM characters within that
rectangle with whitespace. This is only used to clear the player character's text box before Shinki's final いくよ‼box. Shinki has two consecutive text boxes in all 4 scripts here, and ZUN probably wanted to clear the otherwise blue text to imply a dramatic pause before Shinki's final sentence. Nice touch. (You could, however, also use it after a box-ending 0xFF command to mess with text RAM in
general.) |
|
| \# | Quits the currently running loop. This returns from either the text loop to the command loop, or it ends the dialog sequence by returning from the command loop back to gameplay. If this stage of the game later starts another dialog sequence, it will start at the next script byte. | |
| \$ | Like \#, but first waits for any key to be
pressed. |
|
| 0xFF | Behaves like TH04's \$ in the text loop, and like
\# in the command loop. Hence, it's not possible in TH05 to
automatically end a text box and advance to the next one without waiting
for a key press. |
At the end of the day, you might criticize the system for how its landmines
make it annoying to mod in ASCII text, but it all works and does what it's
supposed to. ZUN could have written the cleanest single and central
Shift-JIS iterator that properly chunks a byte buffer into halfwidth and
fullwidth codepoints, and I'd still be throwing it out for the upcoming
non-ASCII translations in favor of something that either also supports UTF-8
or performs dictionary lookups with a full box of text.
The only actual bug can be found in the input detection, which once
again doesn't correctly handle the infamous key
up/key down scancode quirk of PC-98 keyboards. All it takes
is one wrongly placed input polling call, and suddenly you have to think
about how the update cycle behind the PC-98 keyboard state bytes
might cause the game to run the regular 2-frame delay for a single
2-byte chunk of text before it shows the full text of a box after
all… But even this bug is highly theoretical and could probably only be
observed very, very rarely, and exclusively on real hardware.
The same can't be said about TH02 though, but more on that later. Let's
first take a look at its data, which started out much simpler in that game.
The STAGE?.TXT files contain just raw Shift-JIS text with no
trace of commands or structure. Turning on the whitespace display feature in
your editor reveals how the dialog system even assumes a fixed byte
length for each box: 36 bytes per line which will appear on screen, followed
by 4 bytes of padding, which the original files conveniently use to visually
split the lines via a CR/LF newline sequence. Make sure to disable trimming
of trailing whitespace in your editor to not ruin the file when modding the
text… ![]()
靈夢:あんた、まだ名前も聞いてないの··
······に覚えられないわよ。・・・・・··
里香:あたいは、里香よ。覚えときなさ··
・・・い。・・・・・・················STAGE5.TXT with visualized whitespace.
These also demonstrate how the CR/LF newlines only make up 2 of the 4
padding bytes, and require each line to be padded with two more bytes; you
could not use these trailing spaces for actual text. Also note how
the exquisite mixture of fullwidth and halfwidth spaces demands the text to
be viewed with only the most metrically consistent monospace fonts to
preserve the intended alignment. 🍷 It appears quite misaligned on my phone.
Consequently, everything else is hardcoded – every effect shown between text
boxes, the face portrait shown for each box, and even how many boxes are
part of each dialog sequence. Which means that the source code now contains
a
long hardcoded list of face IDs for most of the text boxes in the game,
with the rest being part of the
dedicated hardcoded dialog scripts for 2/3 of the
game's stages.
Without the restriction to a fixed set of scripting commands, TH02 naturally
gravitated to having the most varied dialog sequences of all PC-98 Touhou
games. This flexibility certainly facilitated Mima's grand entrance
animation in Stage 4, or the different lines in Stage 4 and 5 depending on
whether you already used a continue or not. Marisa's post-boss dialog even
inserts the number of continues into the text itself – by, you guessed it,
writing to hardcoded byte offsets inside the dialog text before printing it
to the screen. ![]() But once again, I have nothing to
criticize here – not even the fact that the alternate dialog scripts have to
mutate the "box cursor" to jump to the intended boxes within the file. I
know that some people in my audience like VMs, but I would have considered
it more bloated if ZUN had implemented a full-blown scripting
language just to handle all these special cases.
But once again, I have nothing to
criticize here – not even the fact that the alternate dialog scripts have to
mutate the "box cursor" to jump to the intended boxes within the file. I
know that some people in my audience like VMs, but I would have considered
it more bloated if ZUN had implemented a full-blown scripting
language just to handle all these special cases.
Another unique aspect of TH02 is the way it stores its face portraits, which
are infamous for how hard they are to find in the original data files. These
sprites are actually map tiles, stored in MIKO_K.MPN,
and drawn using the same functions used to blit the regular map tiles to the
📝 tile source area in VRAM. We can only guess
why ZUN chose this one out of the three graphics formats he used in TH02:
- BFNT supports transparency, but sacrifices one of the 16 colors to do so. ZUN only used 15 colors for the face portraits, but might have wanted to keep open the option to use that 16th color. The detailed backgrounds also suggest that these images were never supposed to be transparent to begin with.
- PI is used for all bigger and non-transparent images, but ZUN would have had to write a separate small function to blit a 48×48 subsection of such an image. That certainly wouldn't have stopped him in the TH01 days, but he probably was already past that point by this game.
- That only leaves .MPN. Sure, he did have to slice each face into 9 separate 16×16 "map" tiles to use this format, but that's a small price to pay in exchange for not having to write any new low-level blitting code, especially since he must have already had an asset pipeline to generate these files.
MIKO_K.PTN, arranged into a 16×16-tile layout that
reveals how these tiles are combined into face portraits.MPNDEF from -Tom-'s MysticTK conveniently uses
this exact layout in its .BMP output. Earlier MPNDEF
versions crashed when converting this file as its 256 tiles led to an
8-bit overflow bug, so make sure you've updated to the current version
from the end of October 2023 if you want to convert this file yourself.
The format stores the 4 bitplanes of each 16×16 tile in order, so good
luck finding a different planar image viewer that would support both
such a tiled layout and a custom palette. Sometimes, a weird
internal format is the best type of obfuscation. 
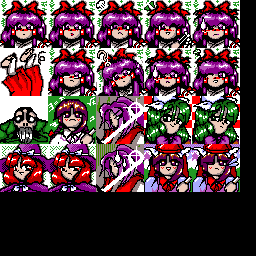
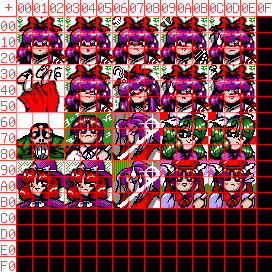
And since you're certainly wondering about all these black tiles at the edges: Yes, these are not only part of the file and pad it from the required 240×192 pixels to 256×256, but also kept in memory during a stage, wasting 9.5 KiB of conventional RAM. That's 172 seconds of potential input replay data, just for those people who might still think that we need EMS for replays.
Alright, we've got the text, we've got the faces, let's slide in the box and
display it all on screen. Apparently though, we also have to blit the player
and option sprites using raw, low-level master.lib function calls in the
process? ![]() This can't be right, especially because ZUN
always blits the option sprite associated with the Reimu-A shot type,
regardless of which one the player actually selected. And if you keep moving
above the box area before the dialog starts, you get to see exactly how
wrong this is:
This can't be right, especially because ZUN
always blits the option sprite associated with the Reimu-A shot type,
regardless of which one the player actually selected. And if you keep moving
above the box area before the dialog starts, you get to see exactly how
wrong this is:
Let's look closer at Reimu's sprite during the slide-in animation, and in the two frames before:
This one image shows off no less than 4 bugs:
- ZUN blits the stationary player sprite here, regardless of whether the player was previously moving left or right. This is a nice way of indicating that Reimu stops moving once the dialog starts, but maybe ZUN should have unblitted the old sprite so that the new one wouldn't have appeared on top. The game only unblits the 384×64 pixels covered by the dialog box on every frame of the slide-in animation, so Reimu would only appear correctly if her sprite happened to be entirely located within that area.
All sprites are shifted up by 1 pixel in frame 2️⃣. This one is not a bug in the dialog system, but in the main game loop. The game runs the relevant actions in the following order:
- Invalidate any map tiles covered by entities
- Redraw invalidated tiles
- Decrement the Y coordinate at the top of VRAM according to the scroll speed
- Update and render all game entities
- Scroll in new tiles as necessary according to the scroll speed, and report whether the game has scrolled one pixel past the end of the map
- If that happened, pretend it didn't by incrementing the value
calculated in #3 for all further frames and skipping to
#8. - Issue a GDC
SCROLLcommand to reflect the line calculated in #3 on the display - Wait for VSync
- Flip VRAM pages
- Start boss if we're past the end of the map
The problem here: Once the dialog starts, the game has already rendered an entire new frame, with all sprites being offset by a new Y scroll offset, without adjusting the graphics GDC's scroll registers to compensate. Hence, the Y position in 3️⃣ is the correct one, and the whole existence of frame 2️⃣ is a bug in itself. (Well… OK, probably a quirk because speedrunning exists, and it would be pretty annoying to synchronize any video regression tests of the future TH02 Anniversary Edition if it renders one fewer frame in the middle of a stage.)
ZUN blits the option sprites to their position from frame 1️⃣. This brings us back to 📝 TH02's special way of retaining the previous and current position in a two-element array, indexed with a VRAM page ID. Normally, this would be equivalent to using dedicated
prevandcurstructure fields and you'd just index it with the back page for every rendering call. But if you then decide to go single-buffered for dialogs and render them onto the front page instead…
Note that fixing bug #2 would not cancel out this one – the sprites would then simply be rendered to their position in the frame before 1️⃣.- And of course, the fixed option sprite ID also counts as a bug.
As for the boxes themselves, it's yet another loop that prints 2-byte chunks
of Shift-JIS text at an even slower fixed interval of 3 frames. In an
interesting quirk though, ZUN assumes that every box starts with the name of
the speaking character in its first two fullwidth Shift-JIS characters,
followed by a fullwidth colon. These 6 bytes are displayed immediately at
the start of every box, without the usual delay. The resulting alignment
looks rather janky with Genjii, whose single right-padded 亀
kanji looks quite awkward with the fullwidth space between the name
and the colon. Kind of makes you wonder why ZUN just didn't spell out his
proper name, 玄爺, instead, but I get the stylistic
difference.
In Stage 4, the two-kanji assumption then breaks with Marisa's three-kanji
name, which causes the full-width colon to be printed as the first delayed
character in each of her boxes:
That's all the issues and quirks in the system itself. The scripts themselves don't leave much room for bugs as they basically just loop over the hardcoded face ID array at this level… until we reach the end of the game. Previously, the slide-in animation could simply use the tile invalidation and re-rendering system to unblit the box on each frame, which also explained why Reimu had to be separately rendered on top. But this no longer works with a custom-rendered boss background, and so the game just chooses to flood-fill the area with graphics chip color #0:
For Mima's final defeat dialog though, ZUN chose to not even show the box.
He might have realized the issue by that point, or simply preferred the more
dramatic effect this had on the lines. The resulting issues, however, might
even have ramifications for such un-technical things as lore and
character dynamics. ![]() As it turns out, the code
for this dialog sequence does in fact render Mima's smiling face for all
boxes?! You only don't see it in the original game because it's rendered to
the other VRAM page that remains invisible during the dialog sequence:
As it turns out, the code
for this dialog sequence does in fact render Mima's smiling face for all
boxes?! You only don't see it in the original game because it's rendered to
the other VRAM page that remains invisible during the dialog sequence:
Here's how I interpret the situation:
-
The function that launches into the final part of the dialog script
starts with dedicated
code to re-render Mima to the back page, on top of the previously
rendered planet background. Since the entire script runs on the front
page (and thus, on top of the previous frame) and the game launches into
the ending immediately after, you don't ever get to see this new partial
frame in the original game.
Showing this partial frame would also ensure that you can actually read the dialog text without a surrounding box. Then, the white letters won't ever be put on top of any white bullets – or, worse, be completely invisible if the dialog is triggered in the middle of Reimu-B's bomb animation, which fills VRAM with lots of white pixels.
Hence, we've got enough evidence to classify not showing the back page as a ZUN bug. 🐞 -
However, Mima's smiling face jars with the words she says here. Adding
the face would deviate more significantly from the original game than
removing the player shot, item, bullet, or spark sprites would. It's
imaginable that ZUN just forgot about the dedicated code that
re-rendered just Mima to the back page, but the faces add
something to the dialog, and ZUN would have clearly noticed and
fixed it if their absence wasn't intended. Heck, ZUN might have just put
something related to Mima into the code because TH02's dialog system has
no way of not drawing a face for a dialog box. Filling the face
area with graphics chip color #0, as seen in the first and third boxes
of the Extra Stage pre-boss dialog, would have been an alternative, but
that would have been equally wrong with regard to the background.
Hence, the invisible face portrait from the original game is a ZUN quirk. 🎺
So, the future TH02 Anniversary Edition will fix the bug by showing the back page, but retain the quirk by rewriting the dialog code to not blit the face.
And with that, we've secured all in-game dialog for the upcoming non-ASCII
translations! The remaining 2/3 of the last push made
for a good occasion to also decompile the small amount of code related to
TH03's win messages, stored in the @0?TX.TXT files. Similar to
TH02's dialog format, these files are also split into fixed-size blocks of
3×60 bytes. But this time, TH03 loads all 60 bytes of a line, including the
CR/LF line breaking codepoints in the original files, into the statically
allocated buffer that it renders from. These control characters are then
only filtered to whitespace by ZUN's graph_putsa_fx() function.
If you remove the line breaks, you get to use the full 60 bytes on every
line.
The final commits went to the MIKO.CFG loading and saving
functions used in TH04's and TH05's OP.EXE, as well as TH04's
game startup code to finally catch up with
📝 TH05's counterpart from over 3 years ago.
This brought us right in front of the main menu rendering code in both TH04
and TH05, which is identical in both games and will be tackled in the next
PC-98 Touhou delivery.
Next up, though: Returning to Shuusou Gyoku, and adding support for SC-88Pro recordings as BGM. Which may or may not come with a slight controversy…