- 📝 Posted:
- 🚚 Summary of:
- P0165, P0166, P0167
- ⌨ Commits:
7a0e5d8...f2bca01,f2bca01...e697907,e697907...c2de6ab- 💰 Funded by:
- Ember2528
- 🏷 Tags:
OK, TH01 missile bullets. Can we maybe have a well-behaved entity type, without any weirdness? Just once?
Ehh, kinda. Apart from another 150 bytes wasted on unused structure members,
this code is indeed more on the low end in terms of overall jank. It does
become very obvious why dodging these missiles in the YuugenMagan, Mima, and
Elis fights feels so awful though: An unfair 46×46 pixel hitbox around
Reimu's center pixel, combined with the comeback of
📝 interlaced rendering, this time in every
stage. ZUN probably did this because missiles are the only 16×16 sprite in
TH01 that is blitted to unaligned X positions, which effectively ends up
touching a 32×16 area of VRAM per sprite.
But even if we assume VRAM writes to be the bottleneck here, it would
have been totally possible to render every missile in every frame at roughly
the same amount of CPU time that the original game uses for interlaced
rendering:
- Note that all missile sprites only use two colors, white and green.
- Instead of naively going with the usual four bitplanes, extract the pixels drawn in each of the two used colors into their own bitplanes. master.lib calls this the "tiny format".
- Use the GRCG to draw these two bitplanes in the intended white and green colors, halving the amount of VRAM writes compared to the original function.
- (Not using the .PTN format would have also avoided the inconsistency of storing the missile sprites in boss-specific sprite slots.)
That's an optimization that would have significantly benefitted the game, in contrast to all of the fake ones introduced in later games. Then again, this optimization is actually something that the later games do, and it might have in fact been necessary to achieve their higher bullet counts without significant slowdown.
Unfortunately, it was only worth decompiling half of the missile code right
now, thanks to gratuitous FPU usage in the other half, where
📝 double variables are compared to float literals.
That one will have to wait
📝 until after SinGyoku.
After some effectively unused Mima sprite effect code that is so broken that
it's impossible to make sense out of it, we get to the final feature I
wanted to cover for all bosses in parallel before returning to Sariel: The
separate sprite background storage for moving or animated boss sprites in
the Mima, Elis, and Sariel fights. But, uh… why is this necessary to begin
with? Doesn't TH01 already reserve the other VRAM page for backgrounds?
Well, these sprites are quite big, and ZUN didn't want to blit them from
main memory on every frame. After all, TH01 and TH02 had a minimum required
clock speed of 33 MHz, half of the speed required for the later three games.
So, he simply blitted these boss sprites to both VRAM pages, leading
the usual unblitting calls to only remove the other sprites on top of the
boss. However, these bosses themselves want to move across the screen…
and this makes it necessary to save the stage background behind them
in some other way.
Enter .PTN, and its functions to capture a 16×16 or 32×32 square from VRAM
into a sprite slot. No problem with that approach in theory, as the size of
all these bigger sprites is a multiple of 32×32; splitting a larger sprite
into these smaller 32×32 chunks makes the code look just a little bit clumsy
(and, of course, slower).
But somewhere during the development of Mima's fight, ZUN apparently forgot
that those sprite backgrounds existed. And once Mima's 🚫 casting sprite is
blitted on top of her regular sprite, using just regular sprite
transparency, she ends up with her infamous third arm:
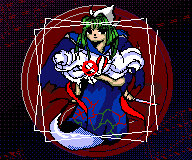
Ironically, there's an unused code path in Mima's unblit function where ZUN assumes a height of 48 pixels for Mima's animation sprites rather than the actual 64. This leads to even clumsier .PTN function calls for the bottom 128×16 pixels… Failing to unblit the bottom 16 pixels would have also yielded that third arm, although it wouldn't have looked as natural. Still wouldn't say that it was intentional; maybe this casting sprite was just added pretty late in the game's development?
So, mission accomplished, Sariel unblocked… at 2¼ pushes. ![]() That's quite some time left for some smaller stage initialization
code, which bundles a bunch of random function calls in places where they
logically really don't belong. The stage opening animation then adds a bunch
of VRAM inter-page copies that are not only redundant but can't even be
understood without knowing the hidden internal state of the last VRAM page
accessed by previous ZUN code…
That's quite some time left for some smaller stage initialization
code, which bundles a bunch of random function calls in places where they
logically really don't belong. The stage opening animation then adds a bunch
of VRAM inter-page copies that are not only redundant but can't even be
understood without knowing the hidden internal state of the last VRAM page
accessed by previous ZUN code…
In better news though: Turbo C++ 4.0 really doesn't seem to have any
complexity limit on inlining arithmetic expressions, as long as they only
operate on compile-time constants. That's how we get macro-free,
compile-time Shift-JIS to JIS X 0208 conversion of the individual code
points in the 東方★靈異伝 string, in a compiler from 1994. As long as you
don't store any intermediate results in variables, that is…
![]()
But wait, there's more! With still ¼ of a push left, I also went for the
boss defeat animation, which includes the route selection after the SinGyoku
fight.
As in all other instances, the 2× scaled font is accomplished by first
rendering the text at regular 1× resolution to the other, invisible VRAM
page, and then scaled from there to the visible one. However, the route
selection is unique in that its scaled text is both drawn transparently on
top of the stage background (not onto a black one), and can also change
colors depending on the selection. It would have been no problem to unblit
and reblit the text by rendering the 1× version to a position on the
invisible VRAM page that isn't covered by the 2× version on the visible one,
but ZUN (needlessly) clears the invisible page before rendering any text.
![]() Instead, he assigned a separate VRAM color for both
the 魔界 and 地獄 options, and only changed the palette value for
these colors to white or gray, depending on the correct selection. This is
another one of the
📝 rare cases where TH01 demonstrates good use of PC-98 hardware,
as the 魔界へ and 地獄へ strings don't need to be reblitted during the selection process, only the Orb "cursor" does.
Instead, he assigned a separate VRAM color for both
the 魔界 and 地獄 options, and only changed the palette value for
these colors to white or gray, depending on the correct selection. This is
another one of the
📝 rare cases where TH01 demonstrates good use of PC-98 hardware,
as the 魔界へ and 地獄へ strings don't need to be reblitted during the selection process, only the Orb "cursor" does.
Then, why does this still not count as good-code? When
changing palette colors, you kinda need to be aware of everything
else that can possibly be on screen, which colors are used there, and which
aren't and can therefore be used for such an effect without affecting other
sprites. In this case, well… hover over the image below, and notice how
Reimu's hair and the bomb sprites in the HUD light up when Makai is
selected:
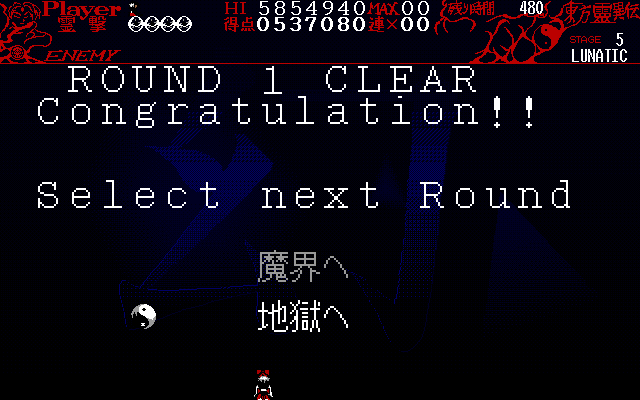
This push did end on a high note though, with the generic, non-SinGyoku version of the defeat animation being an easily parametrizable copy. And that's how you decompile another 2.58% of TH01 in just slightly over three pushes.
Now, we're not only ready to decompile Sariel, but also Kikuri, Elis, and SinGyoku without needing any more detours into non-boss code. Thanks to the current TH01 funding subscriptions, I can plan to cover most, if not all, of Sariel in a single push series, but the currently 3 pending pushes probably won't suffice for Sariel's 8.10% of all remaining code in TH01. We've got quite a lot of not specifically TH01-related funds in the backlog to pass the time though.
Due to recent developments, it actually makes quite a lot of sense to take a break from TH01: spaztron64 has managed what every Touhou download site so far has failed to do: Bundling all 5 game onto a single .HDI together with pre-configured PC-98 emulators and a nice boot menu, and hosting the resulting package on a proper website. While this first release is already quite good (and much better than my attempt from 2014), there is still a bit of room for improvement to be gained from specific ReC98 research. Next up, therefore:
- Researching how TH04 and TH05 use EMS memory, together with the cause behind TH04's crash in Stage 5 when playing as Reimu without an EMS driver loaded, and
- reverse-engineering TH03's score data file format
(
YUME.NEM), which hopefully also comes with a way of building a file that unlocks all characters without any high scores.
